How To Back Up Data Using Windows Backup and File History

Having a backup of all your data is very important since we use so much of it in our daily lives, so it’s handy to have a backup software. At the same time, many of us enjoy not having tons of different backup, optimization, and safety software tools scattered all around our desktops and hard drives. If you are one of these people, learning how to use the Windows onboard backup tools, like File History, is essential to not drowning in a million third-party software tools.
What Are the Windows Backup Tools?
Windows 7 systems let you use the Windows Backup tool, while Windows 8 and 10 feature the File History tool. Both tools are used to automatically store copies of large amounts of data for when you might want to restore older versions of misused or broken data.
Windows Backup tool allows simple backup with a lot of customization options – you can pick each and every folder that gets backed up, choose whether you need a backup of the system image or not, and set a schedule for when your files should be backed up. You’ll find Windows Backup on Windows 7 systems.
File History is a backup tool, that is integrated into all Windows 8 and 10 operating systems. It lets you pick an external storage device or a network storage space for backup, change how often a backup is created and how long are the backups being kept. It also makes restoring older versions of files very easy. Choosing what folders get backed up is a bit more difficult here, though, since there are no specific options to do so and File History will basically backup only the My Documents folder. However, there’s a workaround to this, which will be discussed in the walkthrough below.
Using Windows Backup
1. Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Backup and Restore.
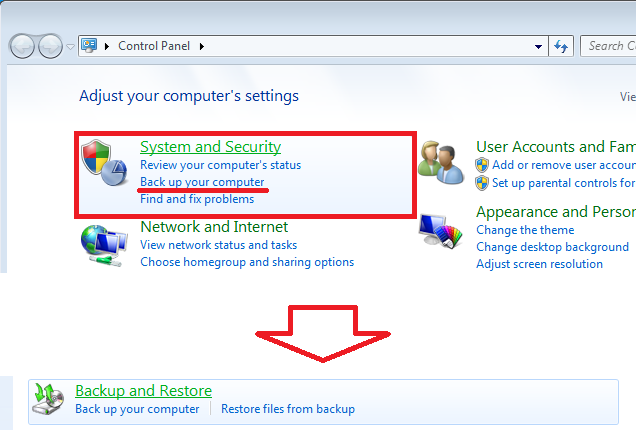
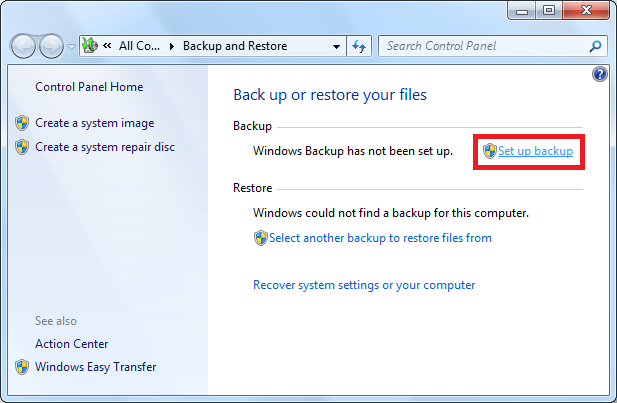
2. Click Set up backup and pick your external hard drive from the list.
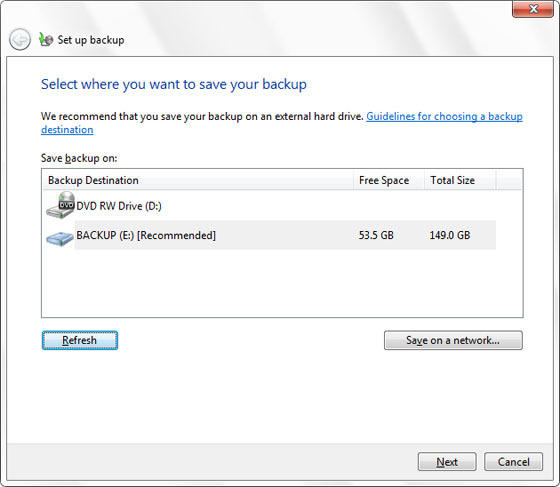
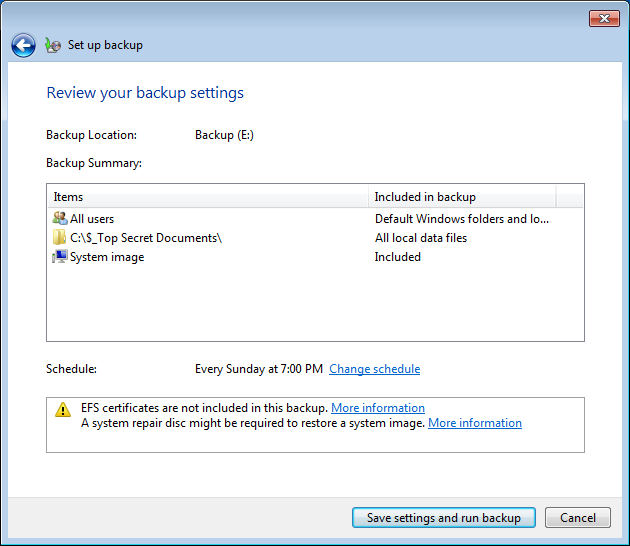
3. Choose whether you want a default backup or a custom one. The default option will backup your desktop, libraries and a system image for restoring your system if it ever breaks down. You can pick each and every folder and library for backup in the Let me choose options, as well as whether you need a system image backup.
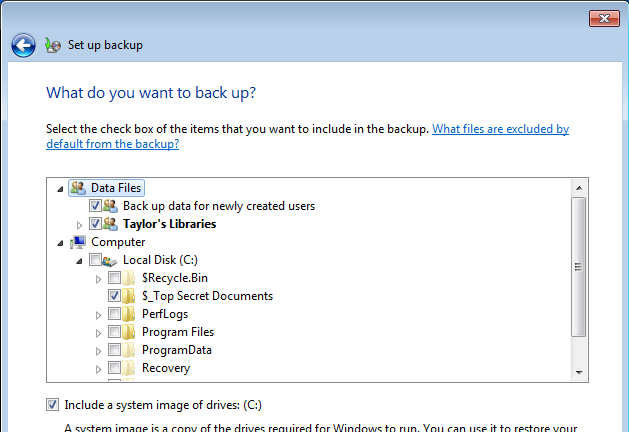
4. Review your choices and set up a backup schedule. After confirming what folders you want to backup, you may review them and choose how often files will get backed up. After confirming your choices, the backup tool will begin backing up your files.
Using File History for Backup
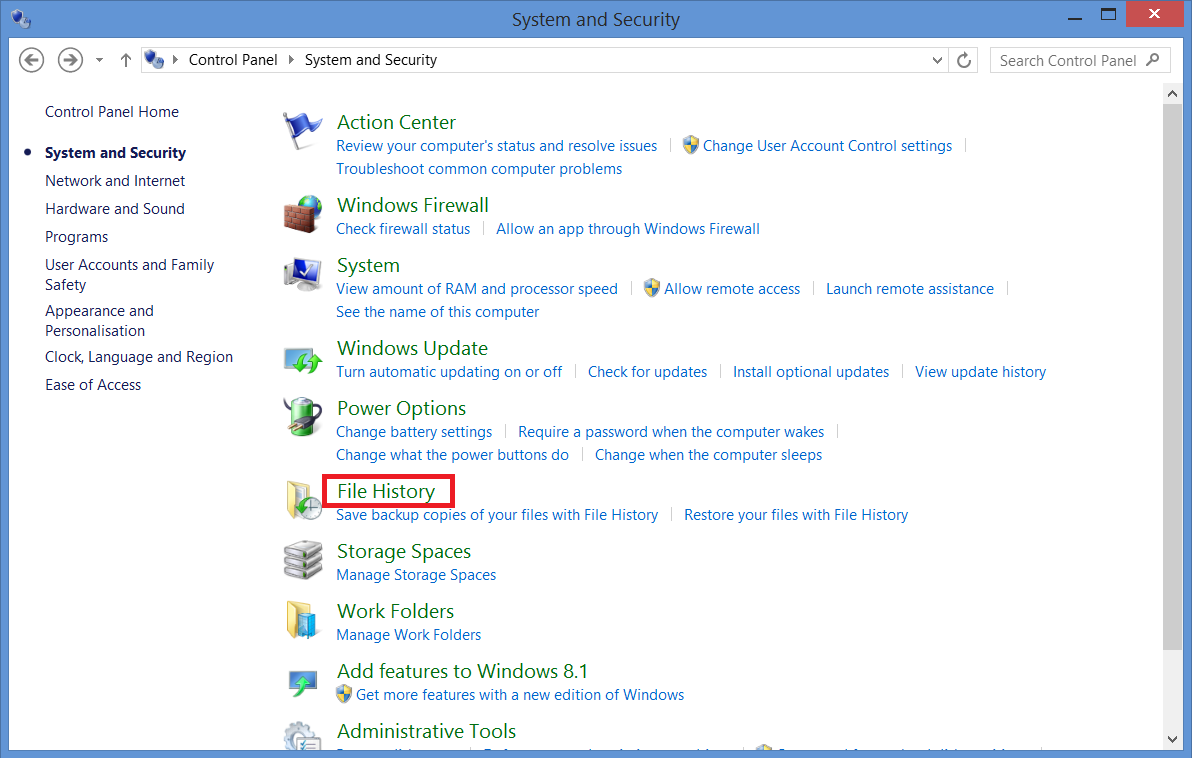
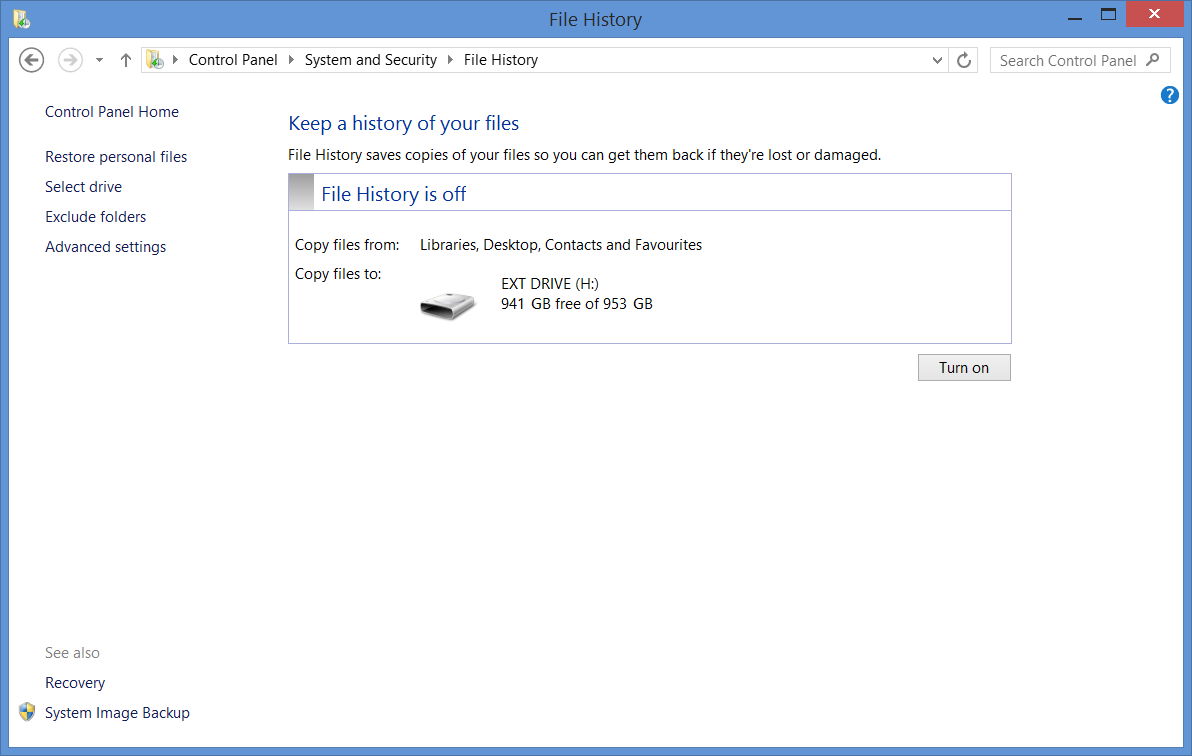
1. Open Control Panel and go to System and Security > File History. You can also access it in the Settings app in the Start Menu, under Update & Security > Backup. Both Control Panel and the Settings app can be easily opened by typing their name into the Start Menu search bar. Make sure you have connected your backup external hard drive before opening File History to make the process faster.
2. Set your external hard drive as the backup drive. when you open File History, it will scan for any external device it can use for backup. If it doesn’t find and show any drives on the front page, go to Select a drive to make file history refresh your options. Note that picking the drive in the Select a drive list will automatically turn on File History. If you want to customize your backup process, go to the following steps first as they will also refresh your drive options.
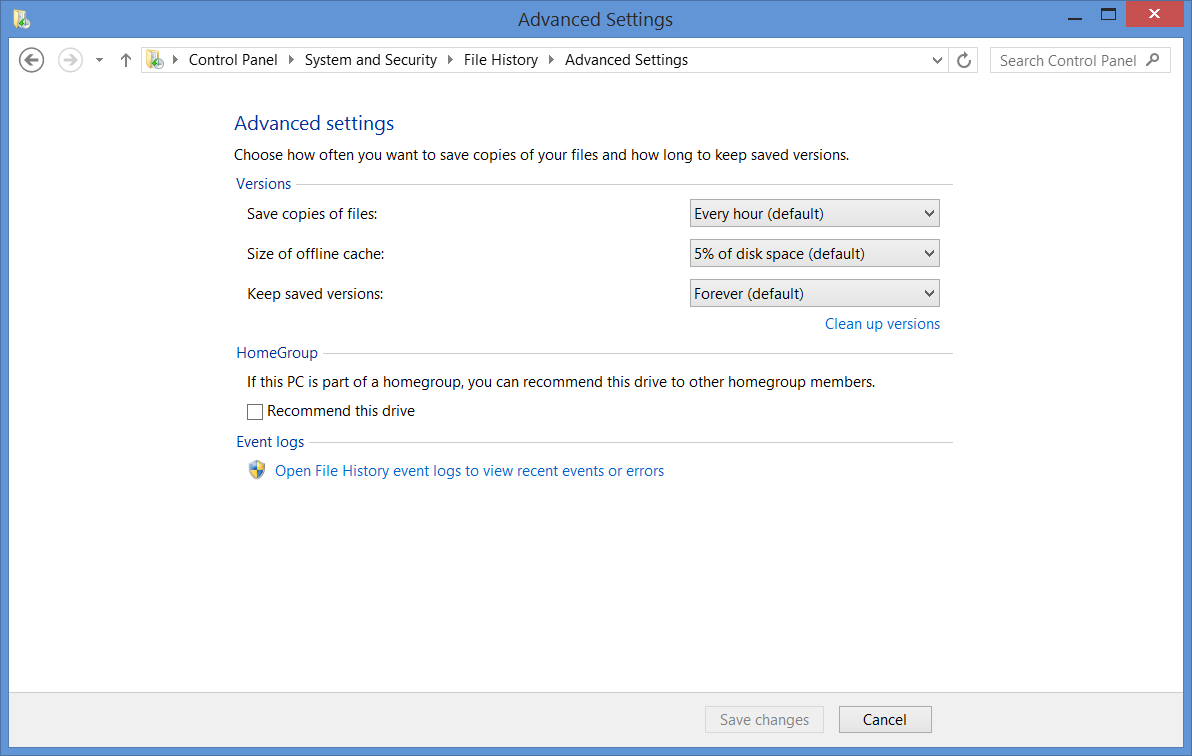
3. Customize the backup process via the Advanced settings and Exclude folders options. Under Advanced settings, you will be presented with the options to change how frequently files get backed up (from once a minute up to once a day) and for how long you want the files to be stored (Forever for the files to never get deleted). Some versions of Windows may present you with an option to change the size of an offline cache (2%-20% of the main drive). The offline cache is a section of your main hard drive that is used to save a part of your backup, which is useful, for example, when you’re traveling without a backup drive and want to have a safe backup of some of the files you’ve recently used. You can also recommend your backup drive to other users of your PC and open a log containing information about the backup process.
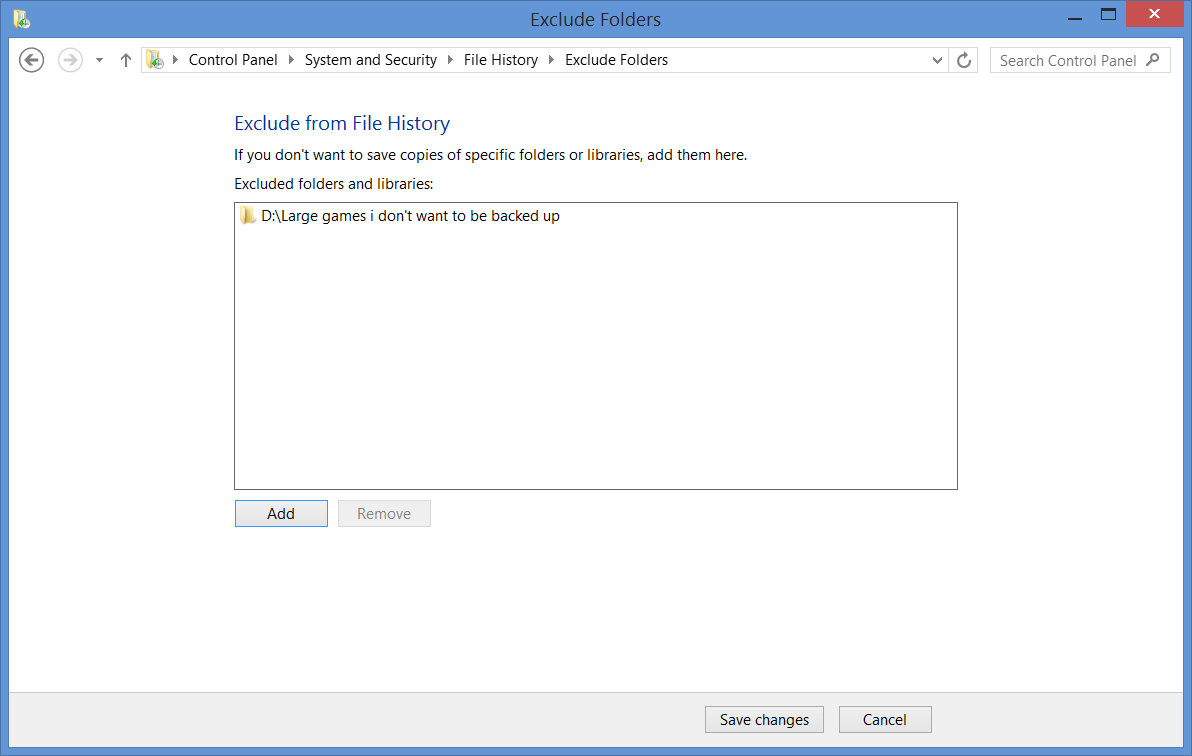
Exclude folders does what it says on the can and lets you browse for any files or folders that won’t get backed up on your external drive.
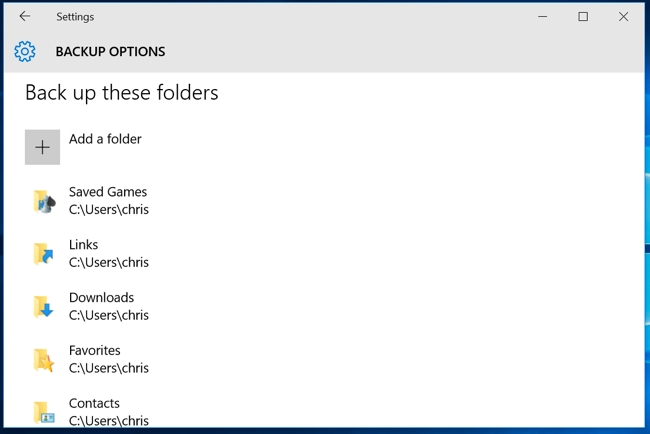
4. Include more folders you want to backup in the Add a folder menu (Win 10), or by adding those folders to an existing or new library (Win 8). Windows 10 allows easy access to the list of folders that it will backup, but doing this in Windows 8 takes a bit more work.
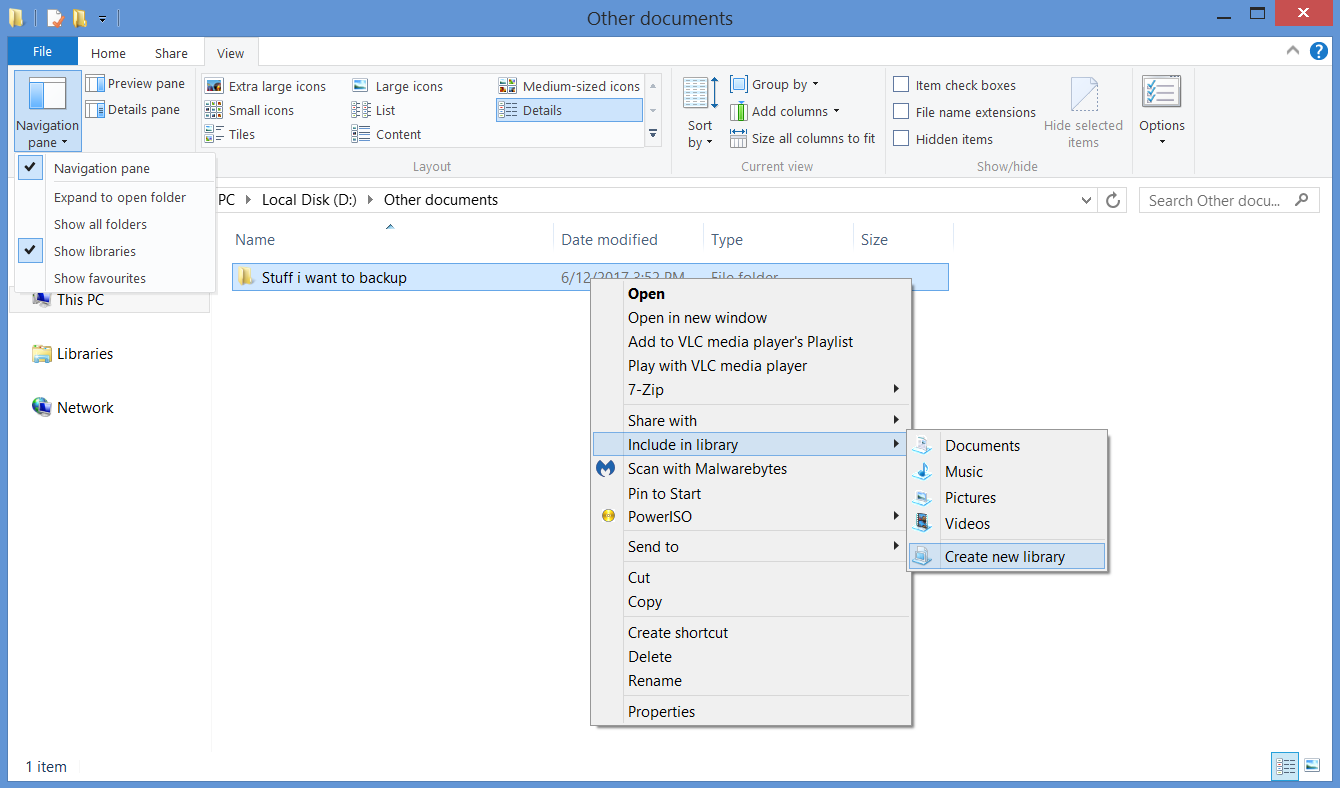
Windows 8 File History by default backs up your libraries (pictures, documents, music etc.) and the desktop. So, while you can’t change the exact folders that will be backed up in Windows 8, you can create your own library that the File History will back up the same way as Music and Pictures. To do so, simply right-click on the folder you want to be backed up, choose Include in library, and then put the folder in one of the existing libraries, or just make a new one (maybe a specific one for backup). It’s possible that you can’t even see (and, in turn, customize) libraries in your version of Windows 8, which can be fixed easily. In any file explorer window, choose the View tab, click the Navigation pane button, and make sure that Show libraries is marked.
Restoring Data From a Backup on Windows
Data recovery using Windows Backup
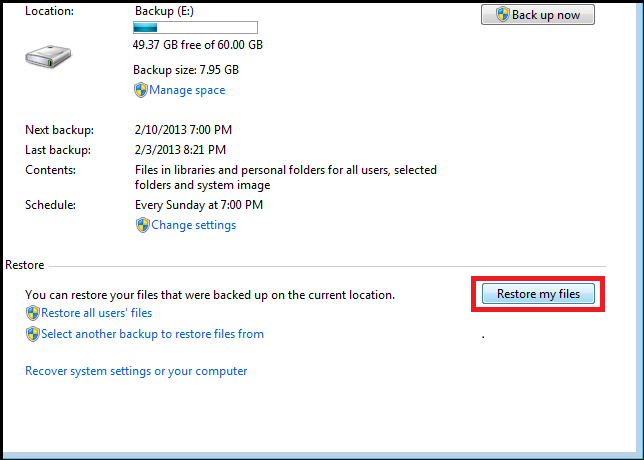
1. Open Windows Backup in Control Panel > System and Security > Backup and Restore. Under Restore options you can either restore all files to a previous backup or click the Restore my files button and browse for a specific file.
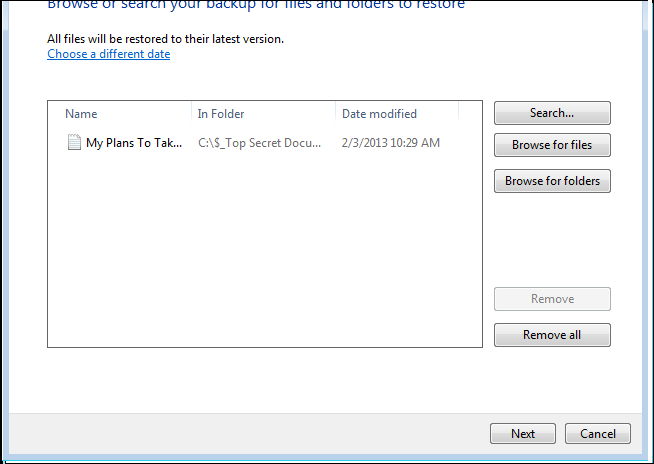
2. In the Restore my files window, you can browse for separate files or folders that need to be restored. Once you’ve picked what files to restore, click Next.
3. After this, you can choose to either write the older version over the newer one in the same location or place the older version in a different folder if you want, for example, to compare the two files. Click Next and the backup version of the file will get copied to wherever you wanted it to go.
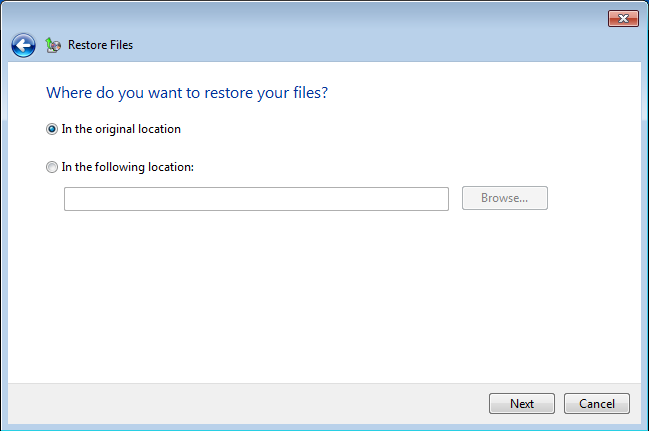
Data recovery using File History
There are two ways to restore previous versions of files with File History – going through a list of backups and their contents or finding the new version of a file and using the Windows File Explorer options.
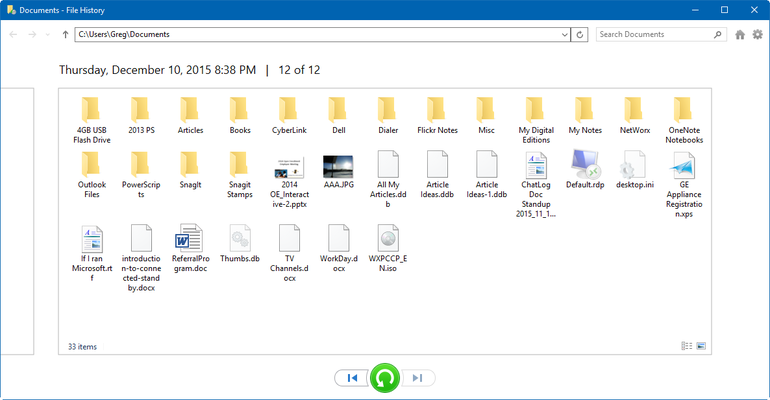
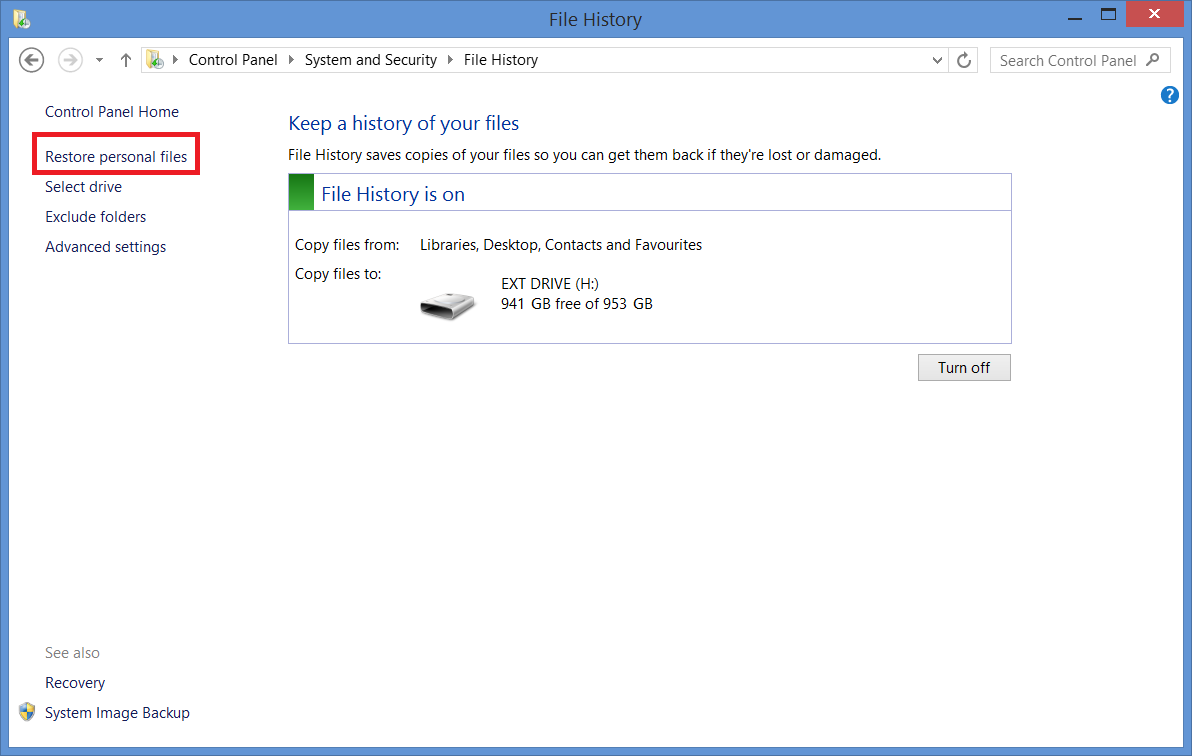
1. In the File History window (under Control Panel > System and Security), pick the Restore personal files option on the left side.This will open a list of all backed up folders and different previous backups (similar to scrolling through pictures, with each picture being one backup). Each page contains one full backup, so you can pick how old the restored version of a file or folder should be.
2. This will open a list of all backed up folders and different previous backups (similar to scrolling through pictures, with each picture being one backup). Each page contains one full backup, so you can pick how old the restored version of a file or folder should be.
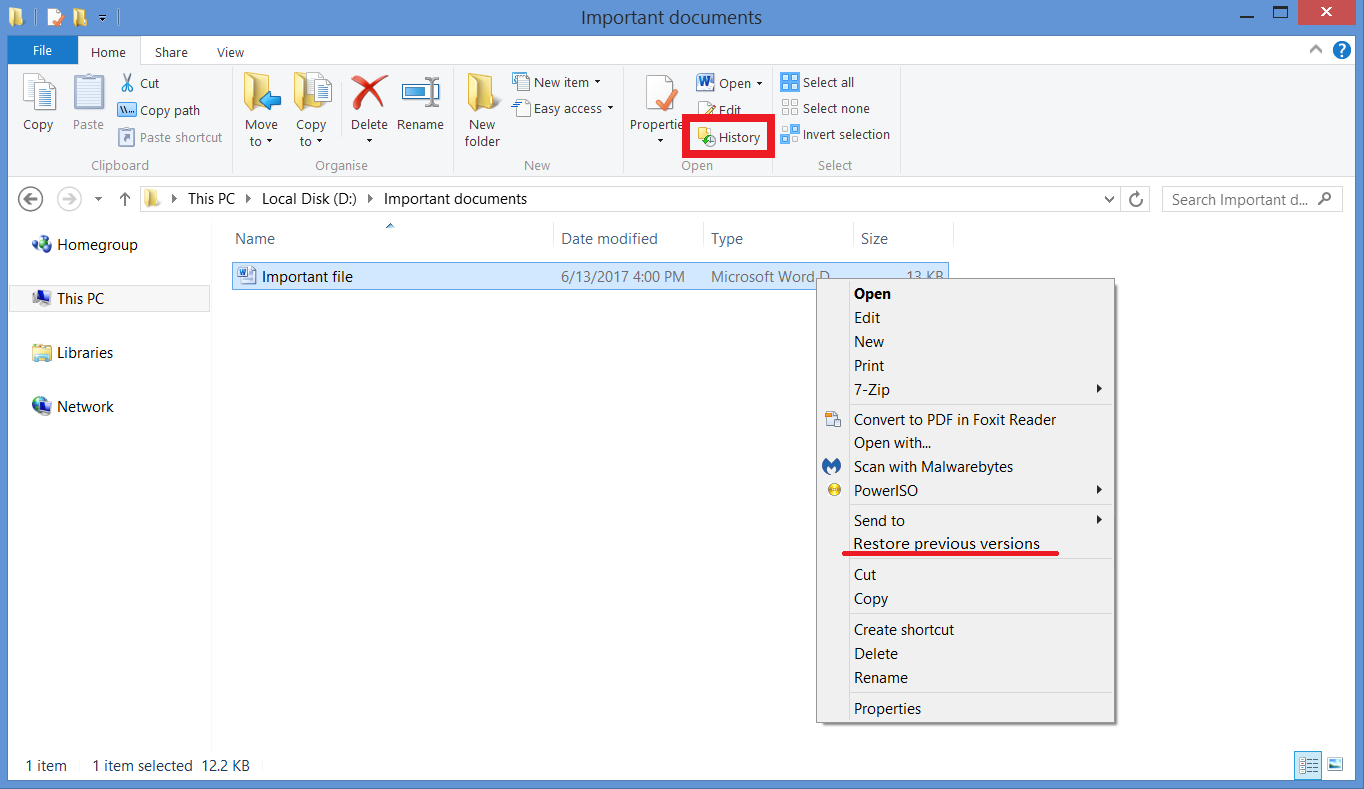
3. The other option is to find the file you want to recover, right-click it and pick Restore previous versions. This will open a list of older versions of this file. To see backups of all files and folders located in the folder you’ve opened, press the History button in the options tab of the File Explorer. This will open a similar “album of backups” to the full backup list in File History menus.


![AOMEI Backupper Standard (Freeware) Review [2018]](https://hddmag.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/AOMEI-Backupper-Featured-2-768x417.png)



